You are given an array nums that consists of positive integers.
The GCD of a sequence of numbers is defined as the greatest integer that divides all the numbers in the sequence evenly.
- For example, the GCD of the sequence
[4,6,16]is2.
A subsequence of an array is a sequence that can be formed by removing some elements (possibly none) of the array.
- For example,
[2,5,10]is a subsequence of[1,2,1,**2**,4,1,**5**,**10**].
Return the number of different GCDs among all non-empty subsequences ofnums.
Example 1:
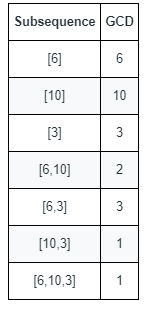
Input: nums = [6,10,3]
Output: 5
Explanation: The figure shows all the non-empty subsequences and their GCDs.
The different GCDs are 6, 10, 3, 2, and 1.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,15,40,5,6]
Output: 7
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 105
- 1 <= nums[i] <= 2 * 105